Continual Learning via Probabilistic Exchangeable Sequence Modelling
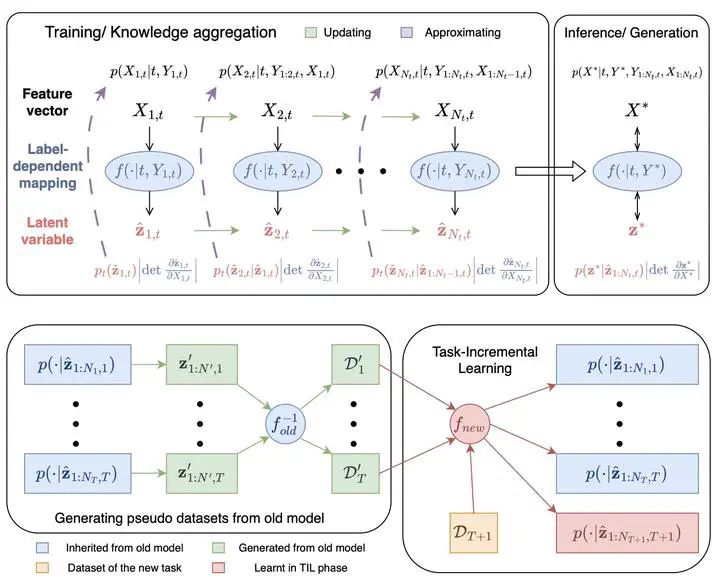
Our research introduces CL-BRUNO, a new framework for continual learning — the ability of AI systems to learn from new information over time without forgetting what they already know.
Unlike many existing methods that are computationally heavy or require storing old data (raising privacy and scalability issues), CL-BRUNO uses a probabilistic, generative approach based on exchangeable sequence modelling. This allows the model to update its knowledge efficiently while maintaining stability, accuracy, and uncertainty awareness — even when past data cannot be retained.
The method unifies multiple continual-learning scenarios (such as learning new classes or tasks) within a single Bayesian framework. It provides interpretable, uncertainty-calibrated predictions and avoids catastrophic forgetting through principled distributional regularization rather than data replay.
Across image-recognition and biomedical benchmarks — including The Cancer Genome Atlas and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor datasets — CL-BRUNO outperforms existing exemplar-free approaches while offering stronger privacy protection and more trustworthy probabilistic outputs.
In short, this work shows that continual learning can be both data-efficient and privacy-conscious, paving the way for reliable AI systems that evolve safely in dynamic, real-world environments.
Lead Investigator: